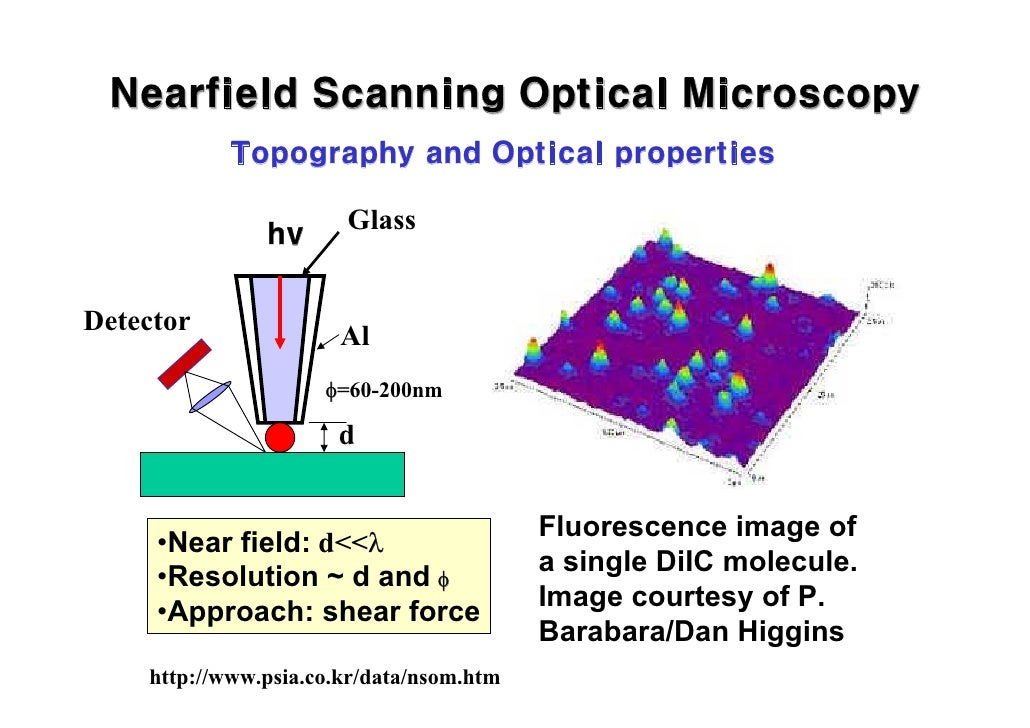
Near field scanning optical microscopy nsom or scanning near field optical microscopy snom is a microscopy technique for nanostructure investigation that breaks the far field resolution limit by exploiting the properties of evanescent waves in snom the excitation laser light is focused through an aperture with a diameter smaller than the excitation wavelength resulting in an evanescent.
Near field optical microscopy ppt.
As a result near field microscopy remains primarily a surface inspection technique 3.
Explaining near field scanning optical microscopy nsom for a class.
The optical microscope often referred to as the light optical microscope is a type of microscope that uses visible light and a system of lenses to magnify images of small samples optical microscopes are the oldest design of microscope and were.
Light diffraction limit of conventional optical microscopy.
Advantages of optical microscopy.
Scanning near field optical microscopy snom is a technique capable of optically investigating the surface of a sample to form either a high resolution two dimensional image or to perform a local spectroscopy.
Trautman thenear field optical interaction betweenasharpprobeandasampleof interest canbe exploitedtoimage spectroscopicallyprobe ormodifysurfacesataresolution downto 12 nm inaccessible by traditional far field techniques.
Actually in real cases the optical resolution λ 500 nm.
Herein we develop a duv scanning near field optical microscope snom with an excitation wavelength of 210 nm.
Microscopy spectroscopy andsurface modification beyondthe diffraction limit eric betzig andjayk.
A fundamental principle in diffraction limited optical microscopy requires that the spatial resolution of an image is limited by the wavelength of the incident light and by the numerical apertures of the condenser and objective lens systems.
Meanwhile near field optics technology is immature in the duv spectral region.
Optical spectroscopy provides a wealth of information on structural and dynamical.
In contrast nsom offers higher resolution around 50 nm or even 30 nm depending on tip.
Di gianfrancesco in materials for ultra supercritical and advanced ultra supercritical power plants 2017.
Far field optics approaches usually suffer from the diffraction limit of light.
Near field scanning optical microscopy nsom.
8 1 4 1 light optical microscopy.
λ 2 250 nm.
Because of this the detector must be placed very close to the sample in the near field zone typically a few nanometers.
Imaging a broad range of samples in a variety of environments.
Near field optical microscopy mahdiar noorbala.
For high spatial resolution the probe must be close to the sample λ 2 250 nm 50nm d 0 61 λ na 4.




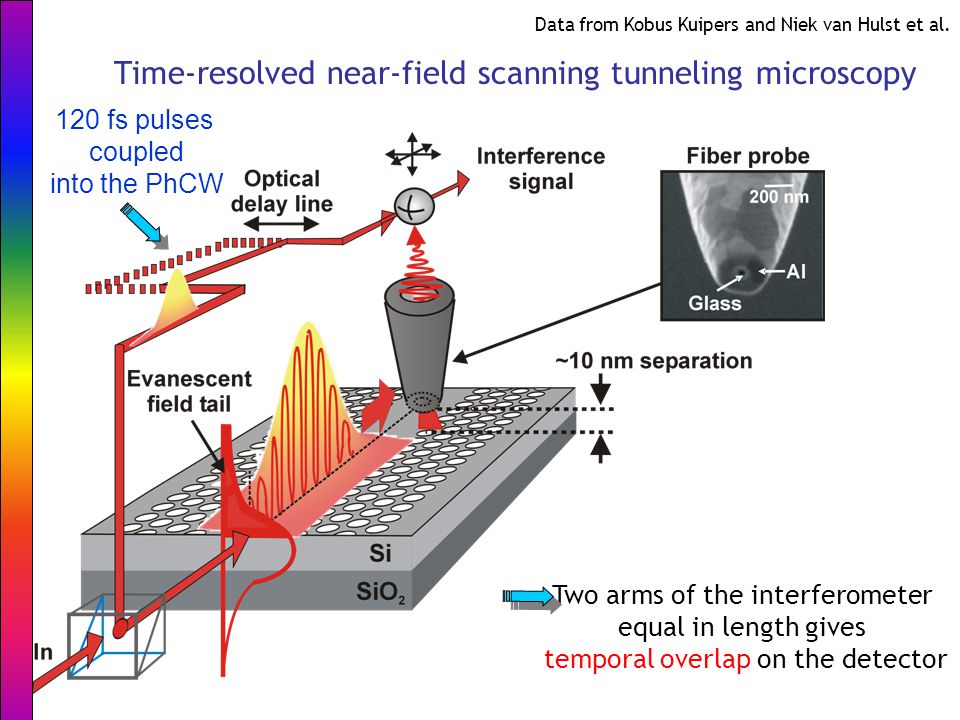

.jpg)