Imaging through wavelength refraction and polarization variations snom measurements on algan and uv leds imaging of exciton wave functions time resolved snom measurements.
Near field scanning optical microscopy applications.
Principle of scanning near field optical microscope and its operation modes.
The concepts governing this method are discussed and the technical challenges encountered in constructing a working nsom instrument are described.
In this review we describe fundamentals of scanning near field optical microscopy with aperture probes.
A new method for high resolution imaging near field scanning optical microscopy nsom has been developed.
Near field scanning optical microscopy is classified among a much broader instrumental group referred to generally as scanning probe microscopes spms.
All spms owe their existence to the development of the scanning tunneling microscope stm which was invented by ibm research scientists gerd binnig and heinrich rohrer in the early 1980s.
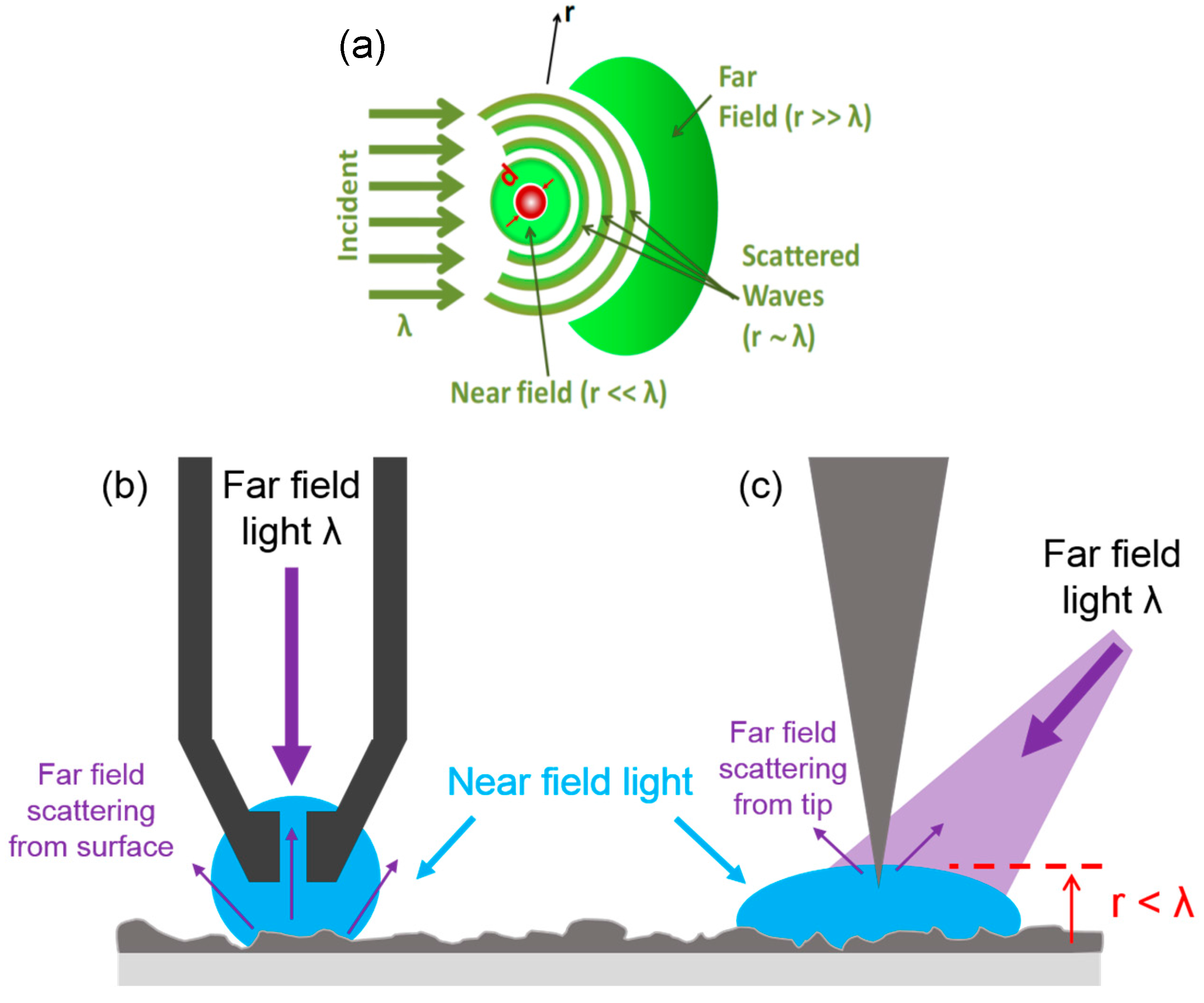
Near field scanning optical microscopy nsom or scanning near field optical microscopy snom is a microscopy technique for nanostructure investigation that breaks the far field resolution limit by exploiting the properties of evanescent waves in snom the excitation laser light is focused through an aperture with a diameter smaller than the excitation wavelength resulting in an evanescent.
It consists an aperture having smaller diameter than the.
Outline optical near field.
Many different methods have been developed in recent years to gain insight into the structure of proteins membranes organelles and cells.
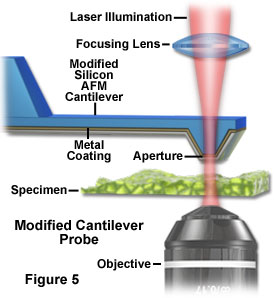
Near field scanning optical microscopy nsom probes.
After the discussion of instrumentation and probe fabrication aspects of light propagation in metal coated tapered optical fibers are considered.
Scanning near field optical microscope is also known as near field scanning optical microscope is used in nanotechnology 16 17.
Probes and distance control.
Here we demonstrate the application of near field scanning optical microscopy nsom for analysis of the structures of typical photosynthetic membrane objects such as chloroplasts and thylakoids from spinach and chromatophores from purple bacteria.



.jpg)